Audi is pursuing the vision of a circular economy

Use of progressive technology
The earth’s resources are limited, so it is important not to consume resources faster than they can be regenerated or reproduced each year by the earth and its ecosystems. Sustainable operations are therefore at the core of the Audi strategy.
One approach from the perspective of AUDI AG is to close material loops in the sense of creating a circular economy and to focus consistently on using progressive technology to start shaping tomorrow’s world today.
“Efficient use of resources is essential, especially considering the transformation toward electric mobility. Closed material loops enable the decoupling of economic growth from the consumption of resources, and also reduce dependencies,” explains Dennis Christian Meinen, a circular economy expert at Audi. A circular economy strives to preserve the value of the product and the materials for as long as possible and to avoid downcycling.
Considering the entire value chain
The full potential of the circular economy can only be exploited if the entire and very complex automotive value chain – which extends from development and material procurement to production and sales and all the way to utilization and recovery – is considered and, to a certain degree, rethought. According to Meinen: “At Audi we want to find sustainable business models that can be implemented to the ultimate benefit of all stakeholders.” As early as 2017, for example, Audi launched an Aluminum Closed Loop in vehicle production, demonstrating just how effective a circular economy can be.
Audi Q4 e-tron: Power consumption (combined) in kWh/100 km: 19.5–16.2CO₂ emissions (combined) in g/km: 0CO₂ emission class: A
Information on electric power consumption and CO₂ emissions in ranges depends on the vehicle’s selected equipment.
Audi Q4 e-tron: Power consumption (combined) in kWh/100 km: 19.5–16.2CO₂ emissions (combined) in g/km: 0CO₂ emission class: A
Information on electric power consumption and CO₂ emissions in ranges depends on the vehicle’s selected equipment.
With a view to bundling the ongoing activities in the company and increasing the spotlight on the topic, Audi established a project house in August 2021 with experts from all of the divisions working together to find solutions – in exchange with external partners, too.
“We cannot achieve the transformation single-handedly,” says Dennis Christian Meinen, considering the complex value chain. “We are working hand in hand with partner companies and research organizations in the project house to take decisive steps toward a circular vehicle. The key signals are laid as early as the product design and not simply when individual parts arrive at the plant gates or even at the recycling stage.”
Already established: Aluminum Closed Loop reduces the consumption of fresh resources in car manufacturing
Already established: Aluminum Closed Loop reduces the consumption of fresh resources in car manufacturing
Audi began its groundbreaking work with the use of aluminum as a body material back in 1994: The first generation of the Audi A8 was the first series-production sedan to have an all-aluminum body.
The material has been used in increasingly more model lines for over 25 years. The production of aluminum is especially energy-intensive, so ensuring that it is used as efficiently as possible is self-evident for Audi.
Today, Audi and its suppliers are able to recycle aluminum offcuts into materials with the same quality as new ones, eliminating a large proportion of the energy-intensive production of new aluminum. In this way, a net total of more than 195,000 metric tons of CO₂ (2020: 165,000; 2019: 150,000) were avoided in 2021. And Audi is aiming to further increase the proportion of secondary material, with the aluminum recovered being fed back into the recycling loop for use in the press shop.
Keeping recycling in mind right from the outset
Who gives any thought to recycling an Audi at the first glimpse of a new one? Audi does! Aspects such as reuse and recyclability are considered as early as the development stage of a vehicle – and thus years before the first series-production vehicle leaves the plant. Statutory requirements create the framework for this planning.1
Each part has to be considered individually when the vehicle reaches its end of life in terms of deciding what further action to take. Initially, of course, the goal should be to reuse or repair. For instance, transmissions can be reconditioned and resold for reuse, while lithium-ion batteries from electric vehicles can start a new life as energy storage devices when they no longer meet the exacting requirements for use in a vehicle.
Using recyclates in new vehicles
Processed plastics derived from a recycling process, otherwise known as recyclates, are being used in more and more vehicles as a contribution to resource conservation. The goal is not just to reduce carbon emissions, but also to use resources efficiently.
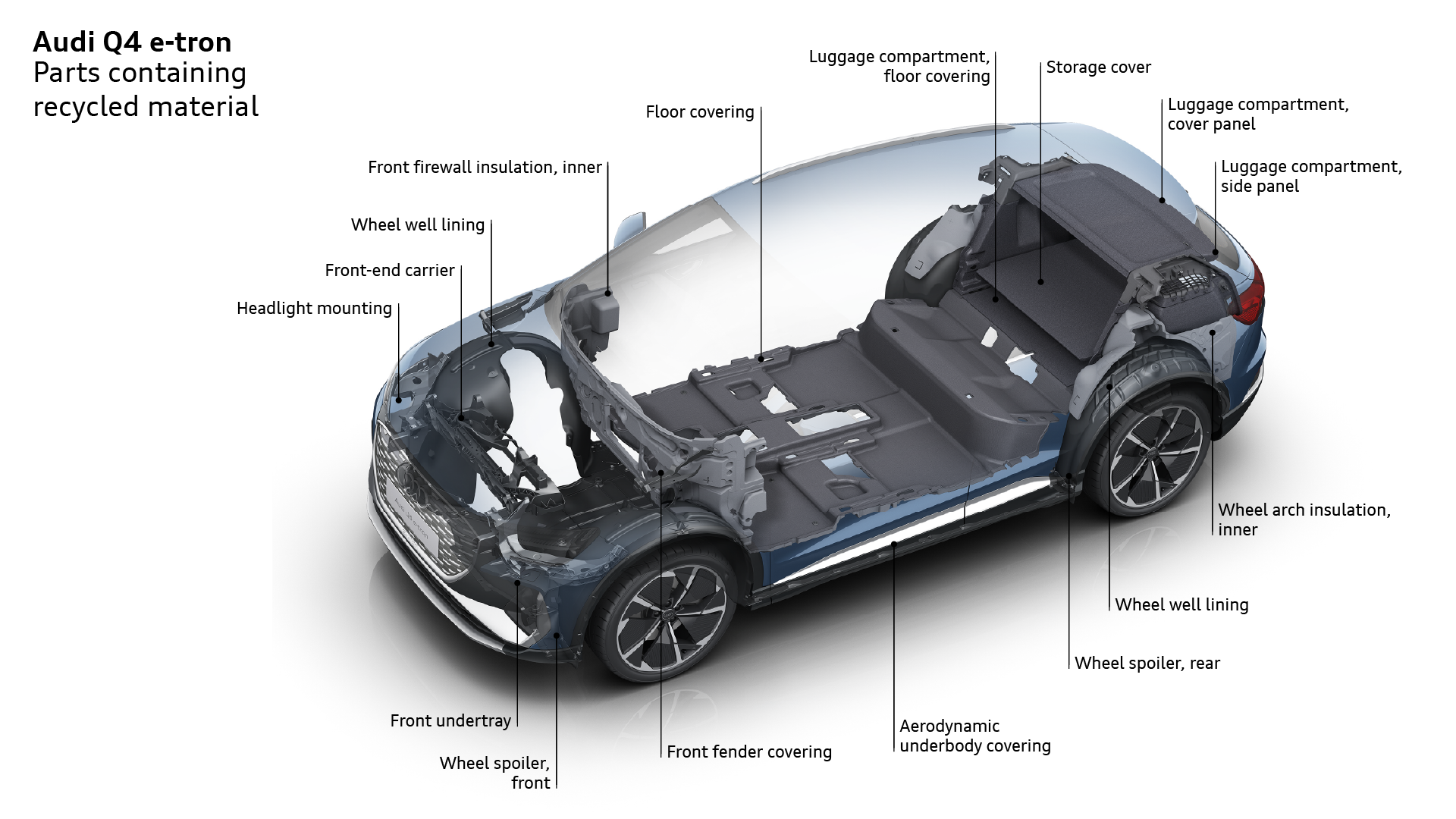
The Audi Q4 e-tron electric SUV has more than two dozen parts that contain a proportion of recycled material. The material from which these parts are manufactured comes from sources such as industrial production waste and is also used to produce components like the front-end carrier – a part that has to meet particularly high mechanical demands. What is more, a significant proportion of the headlight mounts, wheel well liners, fender covers, floor covering and the wheel spoilers is made from secondary raw materials.
Audi Q4 e-tron: Power consumption (combined) in kWh/100 km: 19.5–16.2CO₂ emissions (combined) in g/km: 0CO₂ emission class: A
Information on electric power consumption and CO₂ emissions in ranges depends on the vehicle’s selected equipment.
Audi Q4 e-tron: Power consumption (combined) in kWh/100 km: 19.5–16.2CO₂ emissions (combined) in g/km: 0CO₂ emission class: A
Information on electric power consumption and CO₂ emissions in ranges depends on the vehicle’s selected equipment.
Plastics from mechanical processing in automotive engineering
Plastics from mechanical processing in automotive engineering
Some 250 kilograms of plastic parts are used on average today in an Audi. The plastics used in vehicle engineering are identified by embossings, for example. After they have been shredded and separated from other materials, plastic parts can be converted into synthetic granulate again in a further process.
However, this mechanical recycling of plastic usually reaches its limits when mixed plastic waste is processed and different adhesives and fillers (e.g. glass fibers) or lacquers are used. In addition, the quality of the plastics decreases with each mechanical processing step, to the extent that they can generally no longer be used in vehicle construction and especially not for safety-relevant parts.
Audi’s “Chemical recycling of plastics in automotive engineering” pilot project targeted the creation of smart circular systems for plastics and the establishment of this method as a complement to mechanical recycling and to replace energy recovery.
Chemical recycling of plastics
Can the concept of the Aluminium Closed Loop also work with other materials and with a view to recycling vehicles? This is a challenge especially in terms of mixed plastic waste that cannot be sorted by type – but one that Audi is ready to embrace. Chemical recycling offers very promising results and can contribute to more sustainable production. Audi is working with partner companies from research and industry on this method and successfully completed a pilot project in 2021.
The process is extremely complex, involving collecting, shredding and heating various plastics, which can also contain foreign substances and lacquers. Using pyrolysis technology – a thermochemical conversion process in which the bonds within the molecules are broken down at high temperatures – pyrolysis oil is produced at a temperature of 500 degrees Celsius, while a large proportion of the other substances settle at the bottom as solid matter. Combustion is prevented by extracting oxygen. The pyrolysis oil can then be used to produce plastic components with the same product high quality as new products. This recycled plastic can even be used for safety-relevant parts.
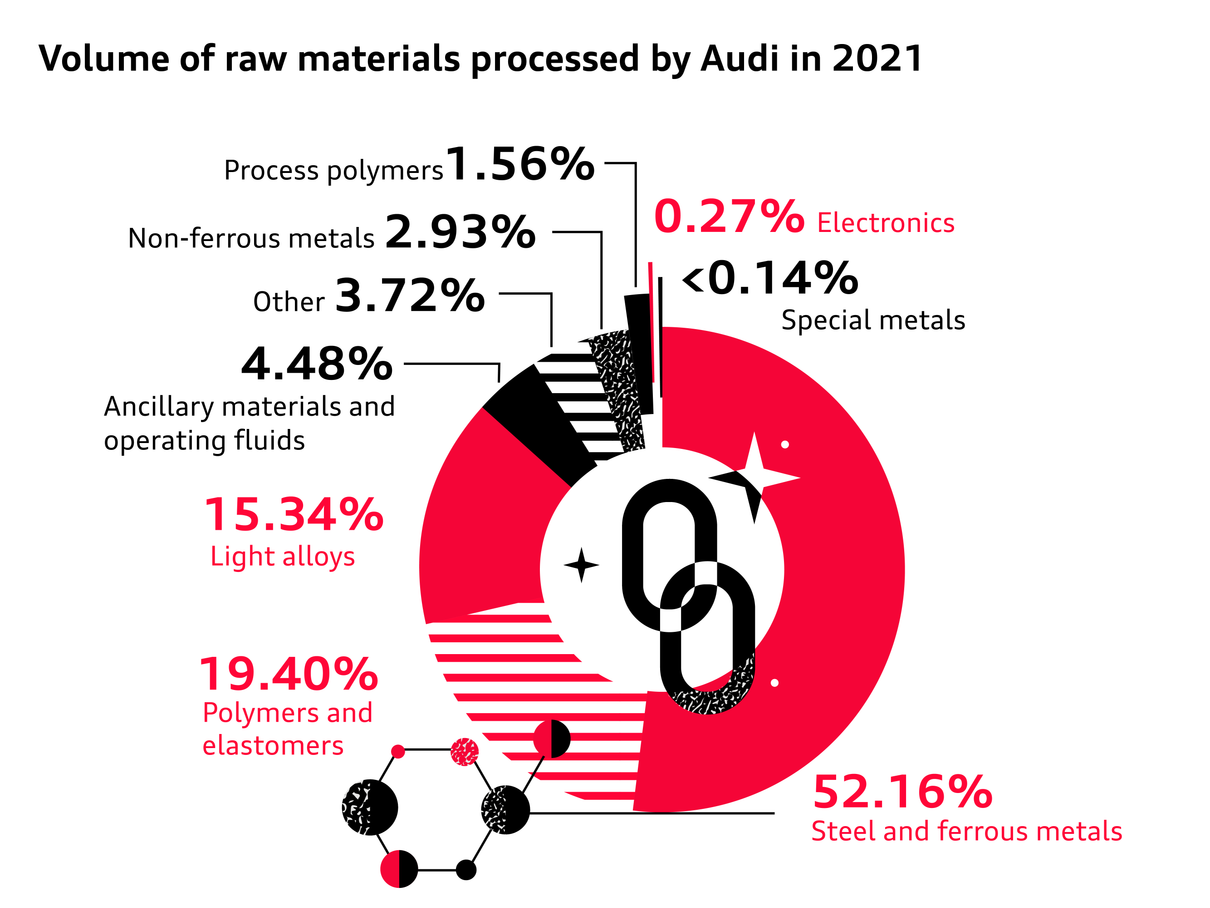
Smart circular systems reduce the use of resources
The chemical recycling of plastic offers enormous potential to significantly increase the number of sustainably produced automobile components. What is more, when used to produce parts, the process should help reduce CO₂ emissions in comparison with the energy recovery2 of plastics. The use of pyrolysis oil is a good example of how the use of resources – in this case crude oil – and the ecological footprint can be reduced while maintaining the same product quality and safety.
The “Chemical recycling of plastics in automotive engineering” pilot project targeted the creation of smart circular systems for plastics and the establishment of this method as a complement to mechanical recycling and replacement of energy recovery.2 Not only was the project a success, but so too was the manner in which Audi supported and drove forward the project: with overarching cooperation between science and industry.