
The currency reform of 1948, not long after the end of the Second World War, marked the beginning of an unprecedented period of economic growth in Germany. At the same time, the appetite for mobility grew – initially for affordable motorised two-wheelers, but soon also for cars. The re-establishment of Auto Union GmbH in Ingolstadt saw the company return to the DKW brand’s roots in vehicle manufacturing. During the 1950s, NSU Werke AG, still an independent company at the time, became the world’s largest manufacturer of two-wheeled vehicles. Soon afterwards, it made a comeback as a car manufacturer.
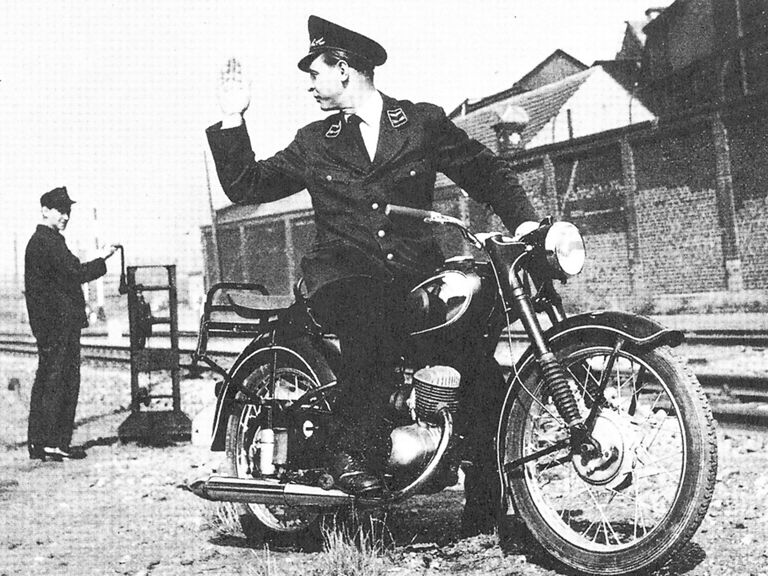
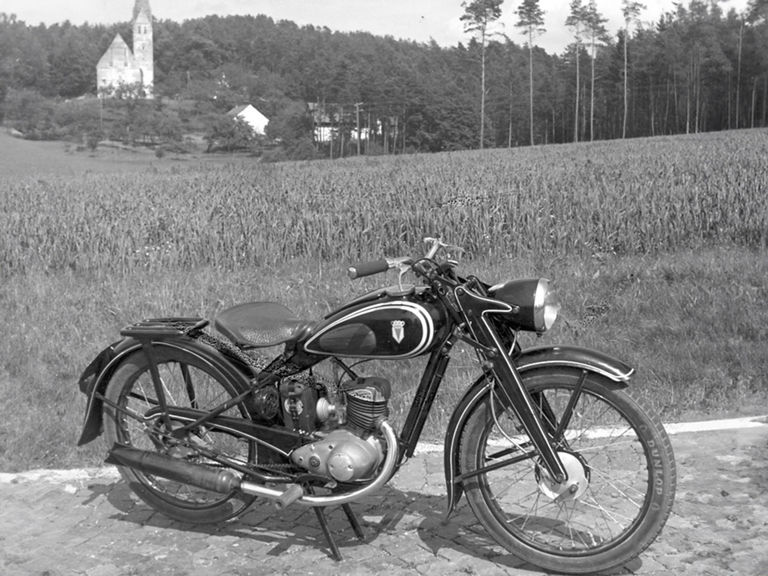
DKW RT 125 W (1949-1957)
More details
DKW RT 125 W:
- Engine: Single-cylinder two-stroke engine
- Displacement: 123 cm³
- Power output: 4.75 PS at 5,000 rpm
- Top speed: 75 km/h
- Length/width/height: 1,985/655/880
- Unladen weight: 73.5 kg
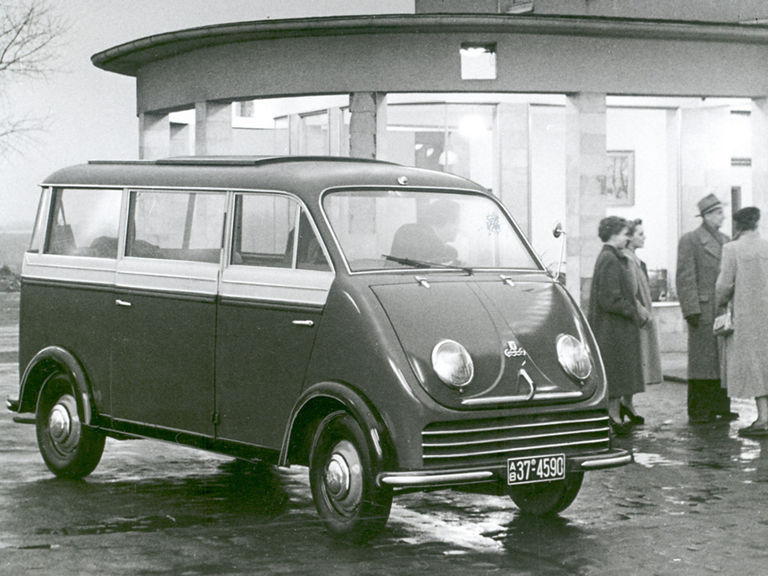
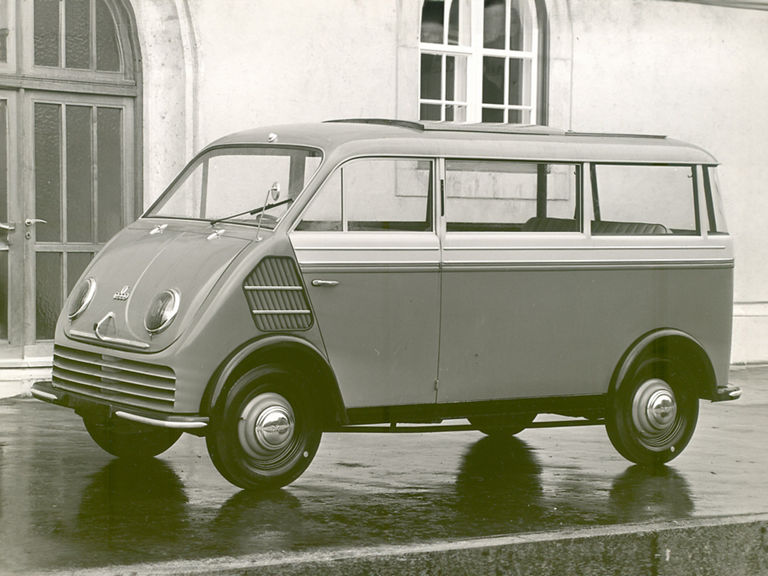
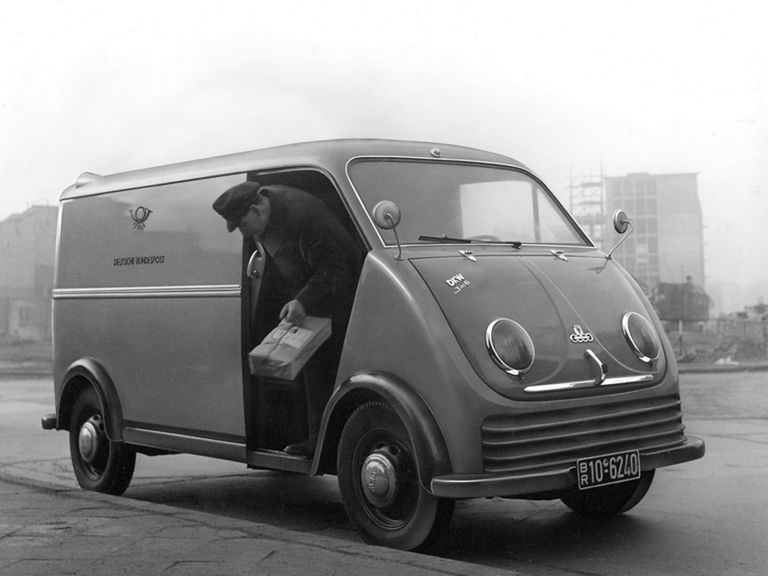
DKW F 89 L Schnelllaster (1949-1962)
More details
DKW F 89 L:
- Engine: Two-stroke petrol engine, 2 inline cylinders, transversely mounted
- Displacement: 684 cm³
- Power output: 20 PS at 3,600 rpm
- Top speed: 78 km/h
- Length/width/height: 3,925/1,550/1,900 mm (box van)
- Unladen weight: 945 kg (box van)
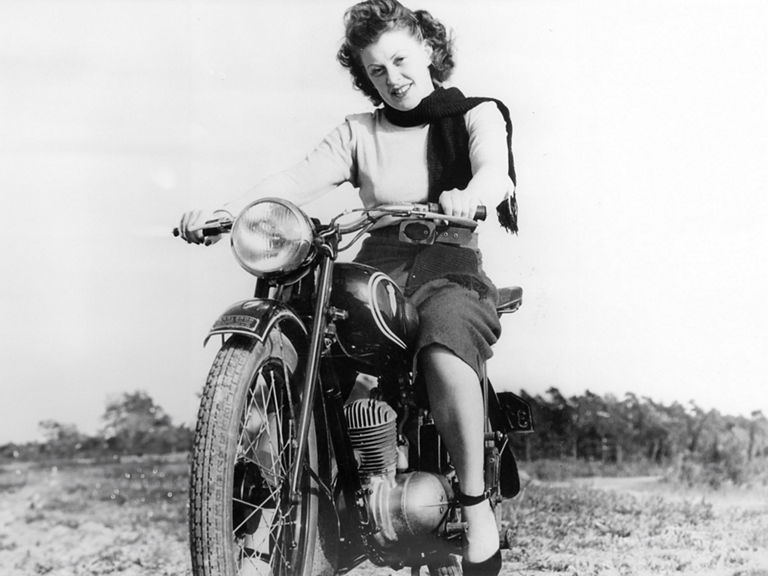
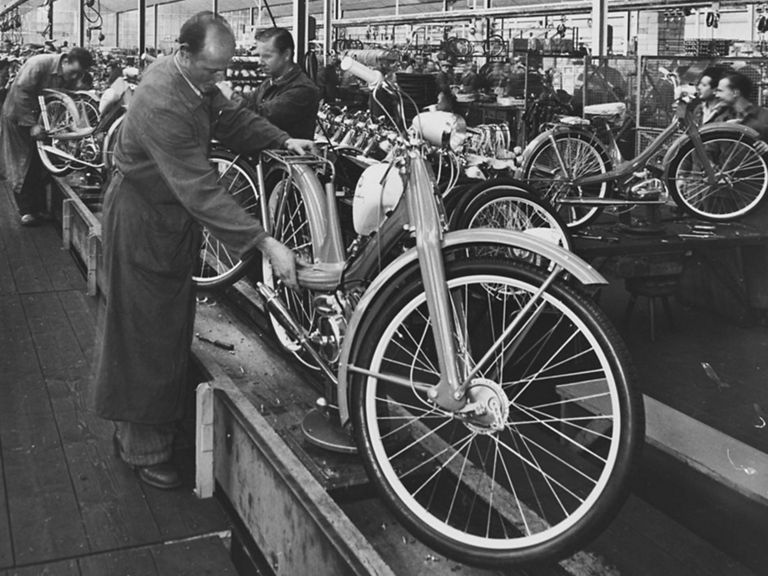
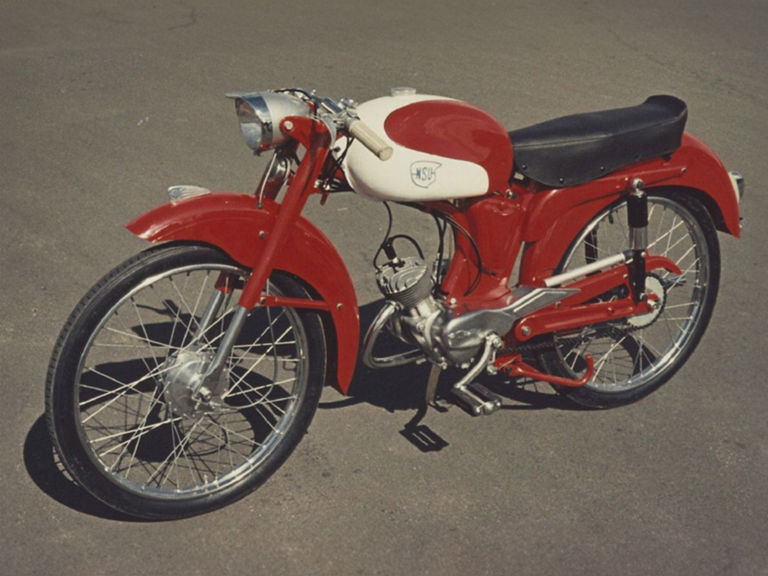
NSU Quickly (1953-1967)
More details
NSU Quickly:
- Engine: Single-cylinder two-stroke engine
- Displacement: 49 cm³
- Power output: 1.3 PS at 5,000 rpm
- Top speed: 40 km/h
- Length/width/height: 1,895/642/960 mm
- Unladen weight: 33 kg
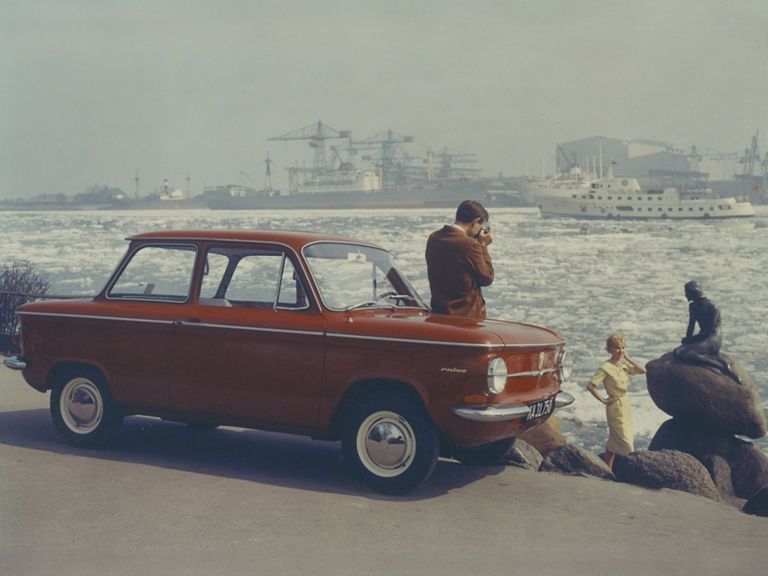
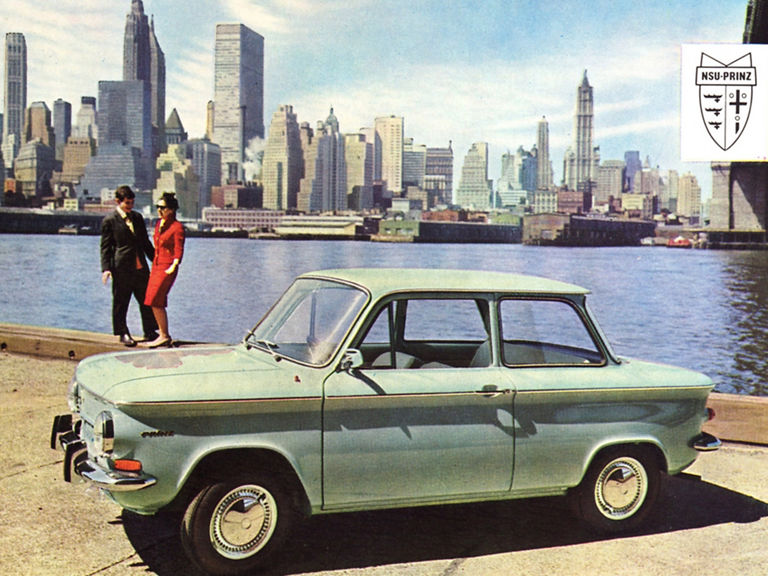
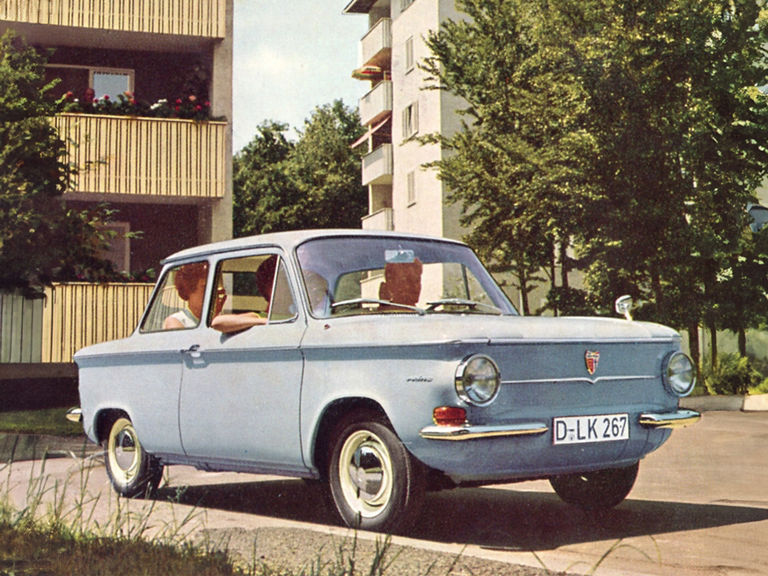
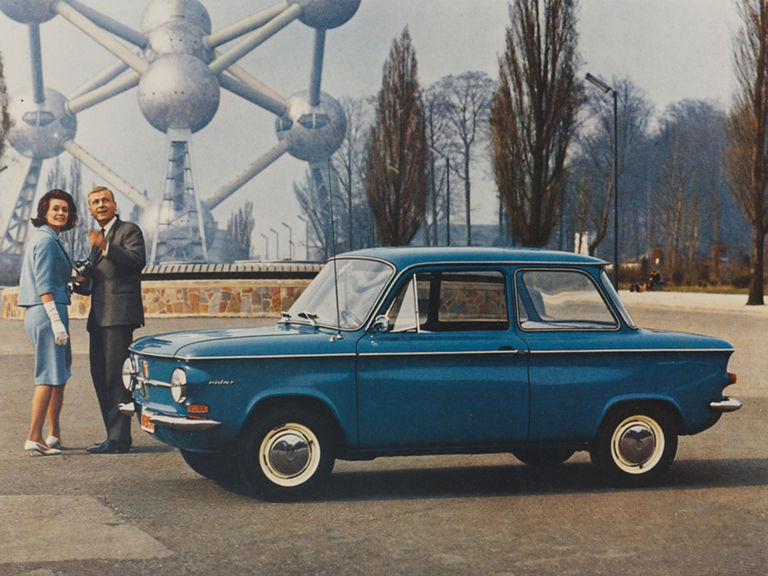
NSU Prinz (1958-1973)
More details
NSU Prinz IV L:
- Engine: Petrol engine, 2 inline cylinders, air-cooled, OHC valve control
- Displacement: 598 cm³
- Power output: 30 PS at 5,500 rpm
- Top speed: 120 km/h
- Length/width/height: 3,440/1,490/1,360 mm
- Unladen weight: 555 kg
Auto Union 1000 SP (1958-1965)
More details
Auto Union 1000 SP Roadster:
- Engine: Two-stroke petrol engine, 3 inline cylinders
- Displacement: 981 cm³
- Power output: 55 PS at 4,500 rpm
- Top speed: 140 km/h
- Length/width/height: 4,170/1,680/1,335 mm (roadster)
- Unladen weight: 950 kg






.jpg?width=768)











-Front-Seitenansicht-(links).jpg?width=768)

-Front-Seitenansicht-(links).jpg?width=768)
.jpg?width=768)
_2.jpg?width=768)



